Free pharmacy material
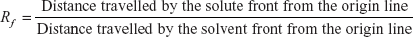


Paper Chromatography
INTRODUCTION
The first chromatograph was invented by Mikhail Semenovich Tsvett. Again it was proposed by the Richard Martin. First, the scientists discovered that the filter paper is used as a substitute for column absorbing powder. Paper chromatography theory was first given by the Archer John porter Martin and Richard Laurence Millington Synge. Later Frederick Sanger applied this method for the determination of insulin structure. Then Melvin Calvin used this technique for the determination of energy producing cells. Watson and Crick used for determination of the DNA structure.
PRINCIPLE
This method is mainly used for the analysis, identification, purification and quantification of mixtures of components into individual compounds. The main principle involved is partition where the substances are distributed between the two liquids. The two liquids are the stationary phase (paper) and the moving liquid is called as the mobile phase.
The movement of the components depends on the nature of the stationary phase and partition coefficient. Based on the separation principle involved, the paper chromatography is divided into two types. They are as follows:
- Paper partition chromatography: In this, paper is used as an inert support with mobile phase.
- Paper adsorption chromatography: In this method, modified papers such as the paper impregnated with the silica or alumina are used for the separation.
THEORY
When a sample of mixture is placed on the paper, where the paper is dipped into the solvent placed in a jar. The solvent moves through the paper based on the capillary action in which the movements of the liquid into the stationary phase (paper) due to forces of adhesion, cohesion and surface tension and the solubility where the solute particles are dissolved in the appropriate solvent. The components with greater affinity towards the stationary phase move faster and the components with less affinity move slower. The components moved to appropriate height then the paper is dried and sprayed with the help of spraying reagents which are specific based on the nature of components. The movement of the components generally expressed by the migration parameters (Rf values). It is defined as the distance travelled by the solute front to that of the solvent front.
Rf value depends on the temperature, solvent and type of the paper used for the separation.
| paper chromatography |
Paper chromatogram
The Rf value is character of partition coefficient. This value is constant for the standard substances. Based on these constant values, the sample is identified with that of the standard substance.
| paper chromatography |
Evaluation of the sample spots with reference standard
Rf values are used in the determination of structure based on their partition coefficients. The following are the factors affecting the Rf values:
- Polarity of the sample.
- The degree of the water saturation of the paper.
- The quality of the paper.
- The purity of the solvent.
- The pH of the solvent.
- Temperature.
Therefore,
log K = log Am/As + log[(1/Rf) -1]
TYPES OF PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY
There are mainly four types of paper chromatography. They are as follows:
- Ascending chromatography: The development of chromatogram is done by travel of the solvent upwards to the paper. In this technique, the mobile phase is placed in the jar at the bottom. The sample is applied on the one edge of the paper leaving 2 cm from the bottom. Then the one side of the paper is emerged in the solvent chamber with the help of hook or strings or plastic clips.
paper chromatography - Ascending chromatogram development
- Descending chromatography: The development of the chromatogram is done by allowing the solvent to travel downwards of the paper. This consists of closed container of appropriate size and shapes which act as a solvent chamber where the mobile phase is placed. The sample spotted paper is inserted in the mobile phase chamber where the spotted end is fixed upside with the help of wires. The only precaution should be taken is mobile phase is equilibrated before elution.
- Descending chromatogram development
- Ascending and descending chromatography: This is the combination of both the above techniques. In this, paper is folded over a glass rod. This allows first the ascending and then descending.
- Ascending and descending chromatography development
- Radial paper chromatography: In this, the sample is applied at the centre of circular filter paper and allows the wick of the paper to be dipped into the mobile phase. This is also called as circular paper chromatography.
radial chromatography development
Radial chromatography developmennt
DETECTION OF THE SPOTS IN PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY
The detection of the spots is carried out by means of the two methods:
- Physical methods: Here the sample spots are detected by the UV radiation or fluorescence radiation.
- Example: Antibiotics are detected when exposed to the UV radiation at 254 nm by using the propanol:water:acetic acid:triethyl amine (75:33:8:8) as the mobile phase.
- Quinine is detected by the fluorescence radiation.
- By chemical methods: These chemical agents are used for the detection based on the nature or functional group present on the sample.
- – Ninhydrin reagent is used for the detection of amino acids (purple spots).
- – Bromocresol green is used for the detection of acidic compounds (yellow spots on green background).
- – Dragendroff's reagent is used for the detection of alkaloids (brown or orange spots).
- – Sodium nitrite is used for the detection of the sulphonamides (purple or red spots).
- – KMnO4 is used as general reagent.
- – Iodine vapour gives brown spots with organic bases.
Choice of the filter paper: Generally Whatman filter papers are used in the paper chromatography. The filter paper contains the 98–99% of cellulose. The following are the factors considered for the selection of filter paper:
- Nature of sample
- Nature of solvent
- Thickness of the paper
- Based on qualitative or quantitative analysis of the sample
The following are the types of papers used in the paper chromatography based on the nature of the sample to be determined:
- Carboxyl papers: These are used for the cationic separation and separation of protonated amines.
- Acetylated papers: These are used for the steroids and pigments separation.
- Ion exchange papers: Used in the ion exchange paper chromatography.
- Kieselguhr papers: These are used for the separation of amines.
- Zirconia papers: Used for the separation of fatty acids.
- Silica papers: Used for the separation of vitamins.
Solvents: The solvents are mainly used to elute the sample. The selection of the solvents is based on the nature of the sample to be separated. Requirements of the solvents are the following:
- The Rf value of the solvent should be 0.05–0.85.
- It should be inert.
- It should be stable.
- It should be free from impurities.
- It should not interfere with the elution.
The following are the common solvents used in the paper chromatography:
- Ethyl alcohol
- Methanol
- Benzene
- Toluene
- N-butanol
- Water
- N-hexane, etc.
Development chamber: These chambers are made up of glass, plastic or stainless steel. Mostly glass chambers are used in the paper chromatography. In the development process, the chamber is saturated with the solvent vapour.
Procedure: The Whatman filter papers are cut into rectangular strips and mark a line on the paper at the 2–3 cm from the bottom. Then spot the paper with sample solution by using the capillary tube. Then place the marked paper in the developing chamber which contains the solvent as the mobile phase. Then the solvent rises up and sample components move along with the mobile phase in upward direction. The movement is based upon the following factors:
- Attraction of the solvent molecules to the cellulose present in the paper.
- Distribution co-efficients of the solute components in the solvent.
Then the paper is removed when the solvent reaches the top of the paper. This level is known as the solvent front.
ADVANTAGES
- Easy way to separate individual components from the mixture
- Inexpensive
- Requires minute samples for analysis
- Less time consumption
- Simple apparatus
DISADVANTAGES
- Less sensitive
- Less accurate
- Only used for the quantitative determinations
- It is not applicable for large quantity of samples
- It is an old technique
APPLICATIONS
- Used in the separation of plant pigments.
- Example: Chlorophyll a and b are separated.
- Used in the determination of sequence in the DNA and RNA molecules.
- Used for the determination of the amino acids.
- Used in the detection of forensic samples.
- Used in the separation of the sugars.
- Used in the separation of the vitamins.
- Used in the separation of the antibiotics.
- Used in the analysis of the metabolites of drugs in the blood and urine samples.
- Used in the separation of the pigments.
- Used in the detection of the unknown compounds.
- Used in the determination of the insecticides in the food components.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- What is Rf value?
- How do you elute the sample by using the radial chromatography?
- What are the factors effecting the separation?
- Which chemical reagent is used for the detection of amino acids?
- Quinine is determined by which detection method?
- What is the difference between the ascending and descending chromatographic methods?
- How the principle of paper chromatography differs with other methods?
- What are the limitations of paper chromatography?
Comments
https://allaboutchemistry123.blogspot.com/2020/09/column-chromatography.html