Free pharmacy material
Electrogravimetry
INTRODUCTION
Luckow first discovered the electrogravimetry for the determination of the copper. Then Alexander Classen first published the paper on the electrogravimetry in 1881. After that, Gibb's was the first founder of the electrogravimetry for the deposition of the metals on the mercury cathode. Electrogravimetry is a method for the separation of the metal ions by using the electrodes. The deposition takes place on the one electrode. The weight of this electrode is determined before and after deposition. This gives the amount of the metal present in the given sample solution.
PRINCIPLE
The main principle involved in this method is the deposition of the solid on an electrode from the analyte solution.
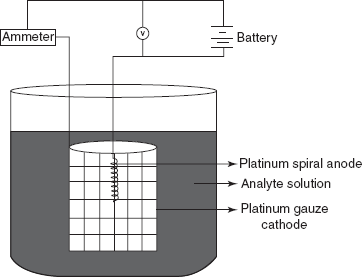
Electrogravimeter
The material is deposited by means of potential application. The electrons are transported to electrode by the following mechanisms:
- Diffusion
- Migration
- Convection
THEORY
A metal is electrolytically deposited on the electrode by increasing the mass of the electrode.
M+2 + 2e−  M(S)
M(S)
Therefore,
Eelectrolysis = Ecathode − Eanode
The electrons deposition is governed by Ohm's and Faraday's laws of electrolysis which states that the amount of the electrons deposited on the electrode is directly proportional to the amount of the current passed through the solution and the amount of different substances deposited is directly proportional to the molar masses divided by the number of electrons involved in the electrolysis process.
That is the current (I) is directly proportional to the electromotive force (E) and is indirectly proportional to the resistance (R).
E = IR
From the above equation, we get the following:
Eelectrolysis = Ecell − IR
Ecell = Ecathode − Eanode
where
Therefore,
Eapplied = Ecathode − Eanode − IR
I = (−Eapplied/R) +1/R(Ecathode − Eanode)
I = (Ecell − Eapplied/R)
I = (−Eapplied/R) + K
where K is the constant.
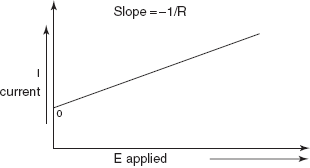
A plot of the current of the applied potential in an electrolytic cell should be straight line with a slope equal to negative reciprocal of the resistance.
Electrogravimetric plot
Types of Electrogravimetry Methods
There are mainly two types of electrogravimetry methods:
- Constant current electrolysis: By name itself it indicates that the constant current is applied for the electrons deposition. The instrument is composed of a cell and direct current source. A 6 V battery, an ammeter and a voltameter are used. The voltage applied is controlled by a resistor.
- Constant current electrogravimeter
Factors Affecting the Deposition
- Current density.
- Temperature.
- The presence of complexing agents.
- Chemical nature of ion.
Applications of Constant Electrolysis
|
Conditions required
|
|
Ag+
|
Alkaline cyanide solution
|
|
Cd+2
|
Alkaline cyanide solution
|
|
Cu+2
|
Acidic solution
|
|
Ni+2
|
Ammonical solution
|
|
Mn+2
|
HCOOH solution
|
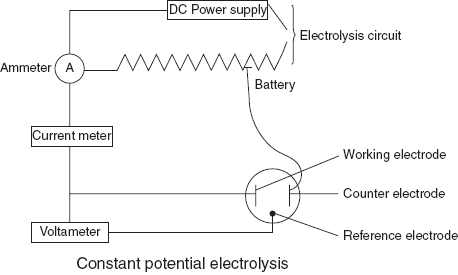
Constant potential electrolysis: In this method, the potential of the cathode is controlled. It consists of two independent electrode circuits that are connected with a common electrode. For the better results, three electrode systems re used.
- Working electrode: used for the deposition of the sample.
- Counter electrode: used as a current sink.
- Reference electrode: maintains the fixed potential despite the changes in solution components.
Constant potential electrogravimeter
Electrode Used in the Electrogravimetry
The electrode used in the electrogravimetry should posses the following characters:
- It should be non-reactive.
- It should be readily ignited to remove the organic matter.
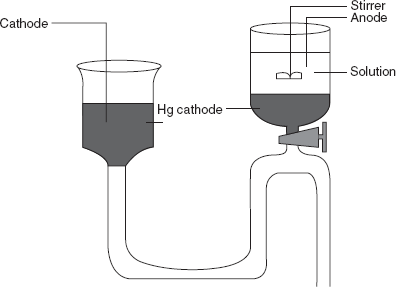
The commonly used electrode is the mercury cathode electrode for the deposition. This has the following advantages:
- It forms the amalgam with number of metals.
- It has a high hydrogen voltage.
In this method, the precipitated elements are dissolved in the mercury. This method is mainly used in the removal of the reduced elements.
Electrodes
APPLICATIONS
- Used in the successive deposition of the metals.
- Example: Cu, Bi, Pb, Cd, Zn and Sn.
- Used in the simultaneous deposition of the metals.
- Used in the electro synthesis.
- Used in the purification process by removing the trace metals from the samples.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- What is the principle involved in the electrogravimetry?
- Explain Ohm's and Faraday's laws.
- Explain the electrolysis process in the electrogravimetry.
- What are the different types of electrogravimetric methods?
- What are factors affecting the deposition of the electrons?
- What are the different types of electrodes used in the electrogravimetry?
- List out the applications of electrogravimetry.
Comments