Free pharmacy material




Coulometry
INTRODUCTION
This method is the measurement of the quantity of the electricity. This is mainly estimated by the reaction of electrode. There are mainly two types of coulometric techniques. They are as follows:
- Controlled potential coulometry.
- Constant current coulometry.
PRINCIPLE
The main principle involved in the coulometry is the measurement of the quantity of the electricity which is directly proportional to the chemical reaction at the electrode. This is given by the Faraday's first law:
where Q is the consumed current; Mr is the relative molecular weight.
THEORY
The coulometric methods are mainly based on the measurement of the quantity of the electricity. The sample which is to be determined undergoes the reaction at the electrode which is measured at the electrode. The completion of the reaction is indicated by the decrease in the current to zero. This can be measured by the coulometer. The substance which is to be determined is first electrolyzed by the constant current. Then the total current is determined by the following equation:
Total current = product current × time
In electrolysis, in the controlled potential coulometry, the quantity of the current Q is given by the following equation:
where It is the current at time t.
Then in the concentration terms it is given by the following equation:
Ct = Coe−kt
where Ct is the concentration of the electrolyte at time t; Co is the initial concentration.
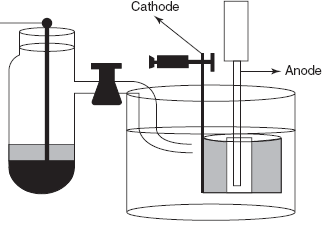
INSTRUMENTATION
In the instrumentation of the coulometry, mainly two types of electrodes are used: one is the reference electrode and another is the working electrode.
Generally saturated calomel electrode is used as the reference electrode. It consists of porous disc at the base of the electrode which is clogged. Above it, the glass tube is filled with the potassium chloride crystals. And above that it is filled with the calomel paste which is prepared by grinding of mercury chloride with pure mercury and minute millilitre of the saturated potassium chloride solution. Then pure mercury is placed in the electrode vessel. The advantages are the following: the easy to construct and highly stable.
Reference electrode
The reaction is the following:
Hg2Cl2 + 2e−  2Hg(l) + 2Cl−
2Hg(l) + 2Cl−
Platinum hydrogen electrode is used as the working electrode.
The apparatus used in the coulometry is as follows:
Working electrode
It consists of the working electrode and the reference electrode and these electrodes are connected to the coulometer. The measured reading is plotted on the graph as follows:
Coulometry titration curve
Two electrodes are immersed in the sample solution which can be measured. Then the constant potential or constant current is passed through the electrode. Next, the chemical reaction takes place at the working electrode and is compared with that of the reference electrode. The completion of the reaction is indicated by the decrease of the current which is measured by the coulometer.
Coulometric Titrations
Constant coulometric method is commonly known as the coulometric titration. In coulometric titrations, the reagent is generated electrically and determined by the current and by the time. It should be of 100% efficiency and the reagent generated should react with the sample solution. The main principle involved in the coulometric titration is the generation of the titrant by electrolysis. Then a large amount of titrant solution is added to the sample solution. Then the sample solution is electrolysed at the anode surface. As the electrolysis proceeds, the anode potential is increased. Then the addition of the titrant solution decreases the potential by decreasing the current. The end point is determined by the any of the end point detection method.
Example: The sample solutions containing the ferrous ions are added to the excess amount of the Ce (III) ion solution.
Fe+2  Fe+3 + e−
Fe+3 + e−
Ce+4 + Fe+2  Ce+3 + Fe+3
Ce+3 + Fe+3
The following are the advantages of the coulometric titrations:
- Standard solutions are not required.
- Reagent is generated.
- No need of the dilution of the sample solution.
- The method is readily adopted than other methods.
The following are the limitations of the coulometric titrations:
- Generation is difficult.
- Inferences are more.
The detection of the end points in the coulometric titrations is done by the following:
- By the chemical indicators: These are added to the sample solution. The only requirement for these reagents should be electroinactive.
- Examples:
- Methyl orange
- Dichlorofluorescein
- Eosin
- Potentiometric end point detection method: When the pair of electrodes are placed in the sample solution it shows the potential difference by the addition of the titrant or by the change in the concentration of the ions. To measure the electromotive force of the electrode, system is measured by the potentiometer or by the electronic voltameter.
- Amperometric method: This method is mainly based on the current produced which is directly proportional to the concentration of the electroactive substance.
- By the spectrophotometric method.
APPLICATIONS
- Used in the determination of the thickness of the metallic coatings.
- Used in the determination of the total anti-oxidant capacity of the anti-oxidants
- Used in the determination of the total carbon in ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- Used in the determination of the picric acid.
- Used in the separation of the nickel and cobalt.
- Used in the analysis of the radioactive materials.
- Used in the determination n-values of the organic compounds.
- Used in the determination of the environment pollutants.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
- What is the principle involved in the coulometry?
- Explain the theory of coulometry.
- Explain in detail about the instrumentation of coulometry.
- What is the principle involved in the coulometric titrations?
- What are the different end point detection methods used in the coulometry?
- List out the applications of coulometry.
Comments
Research Chemical KU Crystal Vendor in USA